Arctic sea ice near all time low
Arctic sea ice is at one of the lowest levels in modern history as scientists continue to warn about the impacts of climate change.
On March 17th, arctic sea ice reached its maximum extent. Meaning ice coverage in the arctic has peaked, and will start decreasing as we head toward summer.
In a video by NASA, arctic ice coverage grows from November to mid-March. You can see it extending south until it reaches its maximum extent. Scientists have since been able to compare this year's ice coverage to other years, and it has been concluded that 2018's maximum arctic ice coverage was the second lowest in history.
Scientists at the National Snow and Ice Data Center and Climate Central have gathered data and graphed the past thirty years to see the trend, and the maximum sea ice per year has decreased drastically, especially in recent years. The last four years alone, have also had the four lowest amounts sea ice on record.
The arctic ice looked like the picture on the left in September of 1984, and it looked like the picture on the right September of 2016. The ice is disappearing, permanently, and this problem is speeding up instead of slowing down.
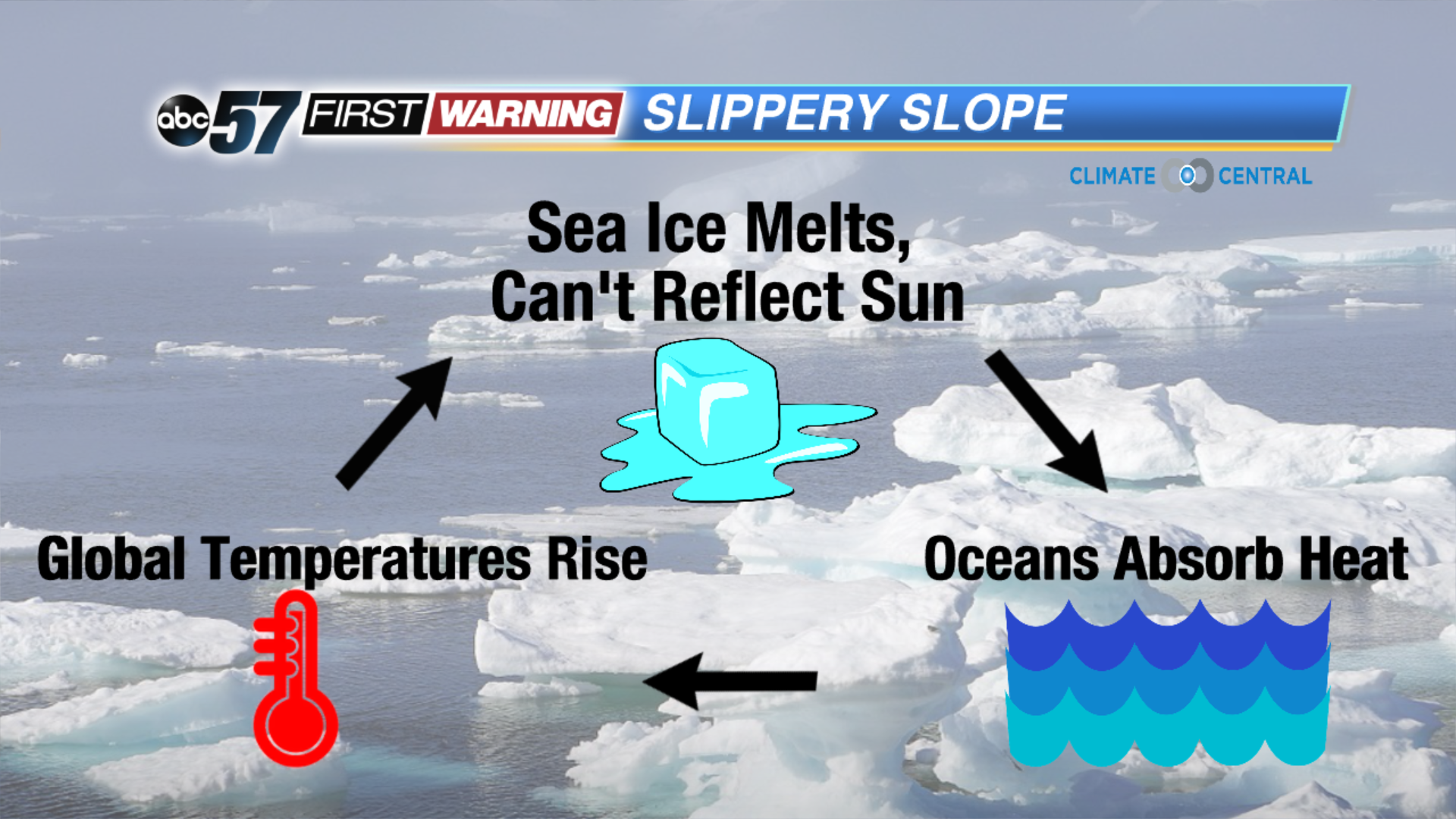
It's a slippery slope. The arctic ice plays a role of deflecting heat off of the surface of the earth, but with the ice melting, the open ocean ends up absorbing that heat. Then, the ocean starts warming up, and in turn, global temperatures rise. With warmer global temperatures, the ice just keeps melting. Research is now being done to see how the lack of arctic ice can affect our seasons, volatile weather patterns, and even severe weather.